

JAPAN
Jiu-Jitsu
Influence from the outside world followed by long periods of isolation have characterised Japan's history.
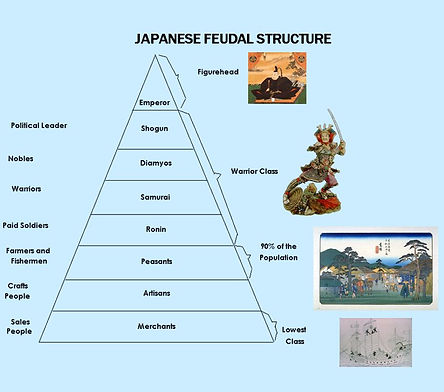
In the feudal era (12th-19th century), a new ruling class of warriors emerged: the samurai. One of the most famous and successful samurai, Oda Nobunaga, conquered numerous other warlords and had almost unified Japan when he was assassinated in 1582. Toyotomi Hideyoshi succeeded him and united the land in 1590 but open war broke out following his death.
In 1854, the US Navy forced the opening of Japan to the outside world. Ensuing economic and political crises led to the Boshin War and the establishment of a centralised state unified under the name of the Emperor (Meiji Restoration).
The Meiji Restoration transformed Japan into an industrialised world power that embarked on a number of military conflicts to expand the nation's sphere of influence, including two Sino-Japanese Wars (1894-1895 and 1937-1945) and the Russo-Japanese War (1904-1905).
On 7 December 1941, Japan attacked the US naval base in Pearl Harbor. This act brought the USA into WWII and, on 8 December, the USA, UK and Netherlands declared war on Japan. After the devastating atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki in 1945, Japan surrendered on 15 August. The war cost Japan millions of lives and left much of the country's industry and infrastructure destroyed.
Japan later achieved exceptional growth to become one of the world's most powerful economies.
